Understanding Internet Technical Terms
What do all of those abbreviations and technical Internet terms mean and what kind of Internet do I need?
Good question! With all of the abbreviations, acronyms, and short names for Internet tech terms out there, it can make your head spin! Here we will give you a quick crash course on some of those terms and how they apply when searching for Internet service for your home or business. You can always contact us at 208-635-4400 with questions. We are happy to help explain all of the terms and how they fit into your needs.
Internet Speeds and Storage
Internet speeds are generally measured using the abbreviations Mb/s and Gb/s (the capitalization of the second letter also has meaning.) A “Mb” means megabit or “million bits” and the “/s” means per second. So an Internet download speed of 7Mb/s would be seven million bits per second. A capital “B” means “bytes” and a lowercase “b” means “bits,” but more on that in a moment.
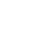
It gets a little confusing here because so many of us are used to hearing “mega” and “giga” when referring to storage space on hard drives, flash drives, or computer RAM. The difference is that while Internet speeds are measured in “bits,” storage is measured in “bytes.” A “byte” is eight “bits.” To put this into perspective an Internet speed of 8 MegaBITS per second is the equivalent of 1 MegaBYTE of data being downloaded to your hard drive or other storage medium or exactly 1/8 of your actual download speed. See below for some tables and terms.
Data Storage Table
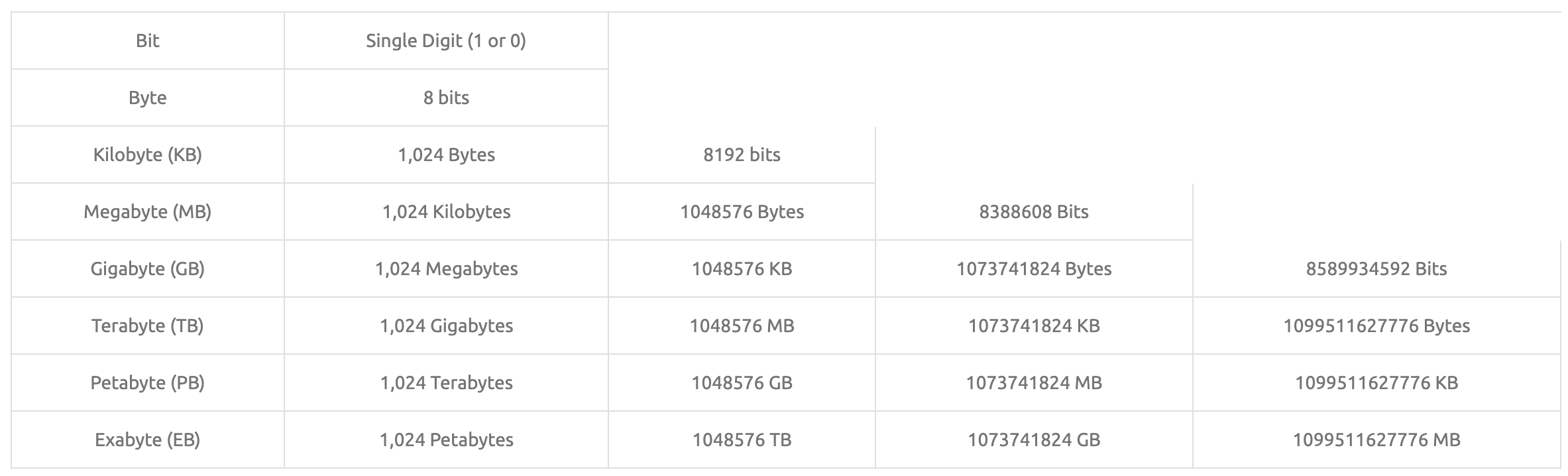
Connection Speed Table
Speed Conversions
- bit = Smallest unit with either the binary digit value of 0 or 1.
- bps = bits per second – data amount to pass a single point/sec.
- Kbps = kilobits per second = 1,000 (one thousand) bits per second.
- Mbps = megabits per second = 1,000,000 (one million) bits per second.
- Gbps = gigabits per second = 1,000,000,000 (one billion) bits per second.
- Tbps = tera bits per second = 1,000,000,000,000 (one trillion) bits per second.
What Kind of Internet and Speeds do I really need?
Picking the right Internet service can sometimes be a pain, and we understand that. There are many different types of service, speeds, and brands out there and picking the right one for your home or business is important. For the most part, we have been taught to believe that speed is the most important thing and that the package with the highest speed at the lowest cost wins, right? Not so fast. When it comes to Internet, speed isn’t always king. The questions and answers below, along with your Intechtel representative, will help you to determine the right type of Internet service for your needs. Call us at 208-635-4400 or email us at info@intechtel.com anytime. We are here to help you make the best decision in choosing your Internet service.
What is the primary purpose of the Internet service? If for business, it is a good idea to look at services that offer uptime guarantees and service level agreements, especially if you are hosting websites or databases that are accessed remotely by customers constantly. Additionally, if you are using Voice over IP (VoIP) for phone service it becomes even more important to look at these things. The kinds and sizes of data you access regularly are a big factor in determining what Internet speed you should buy. Surfing websites and checking emails generally don’t require much speed whereas streaming multiple Netflix videos and downloading large files do require more speed.
Will the Internet service be used primarily for gaming or VoIP? If this is the case, satellite based Internet services will typically be out of the running unless they are your only option based on where you live. Reason being is that most Internet satellites are in geostationary orbits 22,000 miles away from earth. With Internet literally travelling near the speed of light and you take into account the 44,000 mile round trip, it equates to a roughly 1/5 to 1/3 of a second delay when you include the latency from the networks here on earth and when it comes to gaming and VoIP, that delay makes all the difference in the world.
Whats the difference between Cable. DSL, and Fiber Optic Internet?
The primary difference is that DSL is a dedicated connection from the phone company central office and Internet equipment to your DSL modem, your speeds will typically be more consistent than that of cable, but DSL availability is limited by the distance from that central office. Newer VDSL systems are closing the distance and speed gap though and have been deployed by companies like Frontier and CenturyLink.
Cable is typically distributed to your home via nodes in every neighborhood, and then back to the cable company central office thus being a shared connection. In times of high usage by others in your neighborhood, your connection speed and latency could suffer. On the flip side, cable Internet usually offers higher available top speeds than DSL, and is not as distance dependent. Many cable companies also over-provision your speeds, meaning that a 20Mbps connection could test as high as 20% higher.
Fiber optic Internet uses a small optical glass and lasers to transmit data over long distances and incredibly high speeds and with lower latency than Cable, DSL, Wireless, or Satellite. There are several different fiber technologies used by Internet providers today depending on the use case, desired speeds, and more. Fiber optic Internet is quickly becoming the de facto standard in new builds and will eventually supplant DSL and Cable as the leader in Internet service delivery technology. Nearly all large businesses, data centers, etc use fiber optic Internet as their primary means of connecting to the Internet due to its lower latency, higher speeds, and reliability.
Are uptime and reliability the most important factors? If so, considering connections such as a T1, bonded T1, fiber internet, or metro Ethernet may be required. The costs for these services are typically many times that of a basic cable or DSL connection, but offer piece of mind in the form of service level agreements, packet delivery guarantees, and uptime guarantees. When Internet is mission critical to your business, these options are where you want to focus your attention.